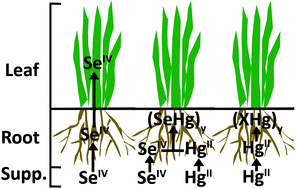
Significant effort has been devoted to studying the mutually protective effect of selenium and mercury in mammals. However, a limited number of studies have investigated the potential selenium–mercury antagonism in plants, which may prove informative for ultimate phytoremediation purposes. In this study, the Allium fistulosum, green onion, was used to investigate the metabolic fate of mercury in conjunction with or exclusion of selenium. The plants were grown in perlite media and supplemented with sodium selenite and mercuric chloride. Total elemental analysisviamicrowave digestion and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICPMS) detection, showed that the A. fistulosum accumulated 50 times more mercury than selenium, both elements were predominately sequestered in the root fraction, and a mutual antagonism was observed. Size exclusion and capillary reversed phase chromatography were coupled to ICPMS to investigate the plant root and leaf extracts. The data suggest a possible selenium–mercury association in a protein containing macromolecule, which is not further metabolized upon translocation to the aerial plant regions. The selenium–mercury association may be formed by combining small selenium molecules, which are normally translocated to the aerial plant regions. Data from enzymatic and acid hydrolysis suggests formation of stable mercury metabolites in the plant when supplemented in conjunction with selenium.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...