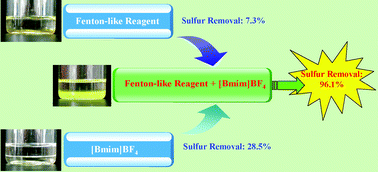
The oxidation of dibenzothiophene (DBT), benzothiophene (BT), and 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene (4,6-DMDBT) in model oil was studied in the extraction and catalytic oxidative desulfurization (ECODS) system at room temperature (30 °C). Various Fenton-like reagents, such as Co2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Mn2+, Cr3+, Fe3+ and H2O2, were screened for desulfurization in ionic liquids. The experimental results demonstrated that the desulfurization system containing anhydrous FeCl3, H2O2, and [bmim]BF4 exhibited high catalytic activity. The sulfur removal of DBT-containing model oil could reach 96.1%, which was obviously superior to mere solvent extraction with [bmim]BF4 (28.5%) or catalytic oxidation without [bmim]BF4 (7.3%). In a combination of extraction and oxidation, the sulfur content decreased from 500 ppm to 5 ppm, when the hydrogen peroxide was added into the desulfurization system in four batches. The catalytic oxidation reactivity of the sulfur-containing compounds was found to be in the following order: DBT > BT > 4,6-DMDBT. Moreover, the desulfurization system could be recycled five times without a significant decrease in activity.