Highly selective detection of Cu2+ utilizing specific binding between Cu-demetallated superoxide dismutase 1 and the Cu2+ ion viasurface plasmon resonance spectroscopy†
Abstract
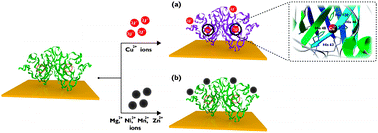
A highly specific interaction between a metal-deficient metalloenzyme and metal ion has been utilized in the selective detection of the metal ion by

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...