Structure-and-mechanism-based design and discovery of therapeutics for cocaine overdose and addiction
Abstract
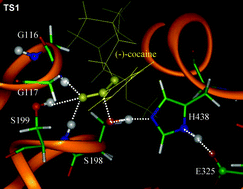
(−)-Cocaine is a widely abused drug and there is currently no available anti-cocaine therapeutic. Promising agents, such as anti-cocaine catalytic antibodies and high-activity mutants of human

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...