Digital microfluidics for cell-based assays
Abstract
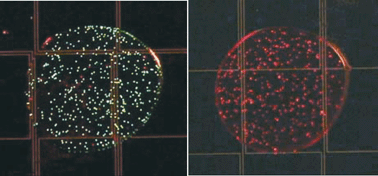
We introduce a new method for implementing cell-based assays. The method is based on digital microfluidics (DMF) which is used to actuate nanolitre droplets of reagents and cells on a planar array of electrodes. We demonstrate that this method is advantageous for cell-based assays because of automated manipulation of multiple reagents in addition to reduced reagent use and analysis time. No adverse effects of actuation by DMF were observed in assays for cell viability, proliferation, and biochemistry. A cytotoxicity assay using Jurkat T-cells was performed using the new method, which had ∼ 20 times higher sensitivity than a conventional well plate assay. These results suggest that DMF has great potential as a simple yet versatile analytical tool for implementing cell-based assays on the microscale.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...