Catalytic asymmetric aldol reactions in aqueous media
Abstract
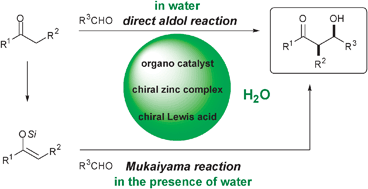
Nature has perfected the stereospecific aldol reaction by using aldolase enzymes. While virtually all the biochemical aldol reactions use unmodified donor and acceptor carbonyls and take place under catalytic control in an aqueous environment, the chemical domain of the aldol addition has mostly relied on prior transformation of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...