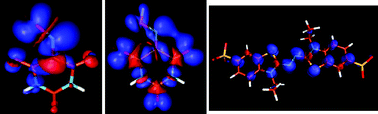
Suitable low molecular-weight compounds, called mediators, can be used in combination with the phenol-oxidase enzyme laccase to indirectly oxidize large organic substrates, such as environmental pollutants, which are not laccase natural substrates. The oxidation of two different synthetic redox mediators, violuric acid (VIO) and 2,2′-azino-bis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) has been studied under catalysis of two laccases from white-rot fungi (Trametes versicolor and Pleurotus ostreatus). VIO was selected as a prototype of the –NOH type of mediators and compared to ABTS, a well-known two-step redox system. To characterize the radical intermediates formed from both mediators after the enzymatic oxidation, a multifrequency EPR approach has been adopted. The radical species have been investigated employing 9.4 GHz (X-band), 34 GHz (Q-band) and 244 GHz (high field) EPR and pulse electron nuclear double resonance (ENDOR) techniques. Theoretical calculations based on density functional theory (DFT/PCM) have been performed to support and further interpret the experimental EPR and ENDOR data. This integrated approach allowed us to obtain a complete characterization of both radicals and to elucidate the type of the radical state (neutral or cationic).
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...