Cationic dinuclear CuII complexes 3 and 4 have been prepared using the novel hydroquinone-based imine chelators 2,5-(iPr2NCH2CH2N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH)2-1,4-(OH)2–C6H2 (1) and 2,5-(pyCH2CH2N
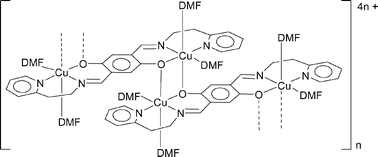
CH)2-1,4-(OH)2–C6H2 (1) and 2,5-(pyCH2CH2N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH)2-1,4-(OH)2–C6H2 (2), respectively (py = 2-pyridyl). X-Ray quality crystals of both complexes were grown from their DMF solutions. The sterically more encumbered compound 3 crystallizes in the form of discrete dinuclear entities with CuII centres in a distorted square-planar ligand environment (one coordination site is occupied by a DMF molecule). The pyridyl derivative 4 features dinuclear hydroquinone-bridged subunits similar to 3. However, the CuII ions are now six-coordinate with two DMF molecules at an axial and an equatorial position of a Jahn–Teller-distorted octahedron. Moreover, the dinuclear subunits are no longer isolated but linked with each other via bridging hydroquinone oxygen atoms which occupy the second apical position of each octahedron. The structure suggests that the magnetic properties of the resulting coordination polymer of 4 could be described by a model valid for dimerized spin chains. As a result of this analysis the antiferromagnetic coupling constants J1/kB = 9.9 K (intradimer) and J2/kB = 0.9 K (interdimer) are obtained. Both in 3 and in 4, the hydroquinone → semiquinone transition of the central bridging unit (E°′ = + 0.57 V, 3; E°′ = + 0.51 V, 4; DMF; vs. SCE) displays features of chemical reversibility. In the case of 4, reduction of CuII centres requires a peak potential of Ep = − 0.42 V.
CH)2-1,4-(OH)2–C6H2 (2), respectively (py = 2-pyridyl). X-Ray quality crystals of both complexes were grown from their DMF solutions. The sterically more encumbered compound 3 crystallizes in the form of discrete dinuclear entities with CuII centres in a distorted square-planar ligand environment (one coordination site is occupied by a DMF molecule). The pyridyl derivative 4 features dinuclear hydroquinone-bridged subunits similar to 3. However, the CuII ions are now six-coordinate with two DMF molecules at an axial and an equatorial position of a Jahn–Teller-distorted octahedron. Moreover, the dinuclear subunits are no longer isolated but linked with each other via bridging hydroquinone oxygen atoms which occupy the second apical position of each octahedron. The structure suggests that the magnetic properties of the resulting coordination polymer of 4 could be described by a model valid for dimerized spin chains. As a result of this analysis the antiferromagnetic coupling constants J1/kB = 9.9 K (intradimer) and J2/kB = 0.9 K (interdimer) are obtained. Both in 3 and in 4, the hydroquinone → semiquinone transition of the central bridging unit (E°′ = + 0.57 V, 3; E°′ = + 0.51 V, 4; DMF; vs. SCE) displays features of chemical reversibility. In the case of 4, reduction of CuII centres requires a peak potential of Ep = − 0.42 V.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH)2-1,4-(OH)2–C6H2 (1) and 2,5-(pyCH2CH2N
CH)2-1,4-(OH)2–C6H2 (1) and 2,5-(pyCH2CH2N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH)2-1,4-(OH)2–C6H2 (2), respectively (py =
CH)2-1,4-(OH)2–C6H2 (2), respectively (py = 

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...