Abstract
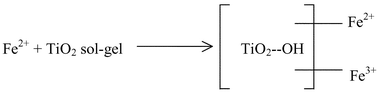
Fe/TiO2 materials at 1 wt% Fe content have been prepared by the addition of aqueous solutions of FeCl2 to titanium n-tetrabutoxide using hydrochloric acid (pH 3) as a hydrolysis catalyst. The obtained gel was thermally treated at 200, 400, 600 and 800 °C. Characterization of the materials was performed by FTIR, UV–Vis, Mössbauer and X-ray powder diffraction. FTIR spectra of the calcined samples showed the presence of highly hydroxylated TiO2. The XRD patterns show the coexistance of brookite, anatase and rutile TiO2 phases in samples treated up to 600 °C. In the sample treated at 800 °C rutile was the only phase observed. UV–Vis spectroscopy revealed that the band gap Eg of the samples increased with increased thermal treatment temperature. Mössbauer spectroscopy showed the coexistance of Fe2+ and Fe3+ on the TiO2 samples treated at high temperatures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...