Diffusion of calcium and barium in alkali alkaline-earth silicate glasses
Abstract
Diffusion of the radioactive isotopes 45Ca and 133Ba in alkali alkaline-earth silicate glasses of compositions 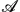 2O·2CaO·4SiO2 with
2O·2CaO·4SiO2 with 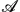 = Li, K, Cs and K2O·2BaO·4SiO2 was investigated at temperatures below the respective glass-transition temperatures. The diffusion profiles of the radiotracers were recorded by means of an ion-beam sputtering technique in conjunction with activity measurements. Analysis of the Ca and Ba profiles is based on the thin-film solution of the diffusion equation and a contribution which takes into account the instrumental broadening of the profiles caused by sputtering effects. The diffusion coefficients of the alkaline-earth ions were determined down to values of as low as 10−21 m2 s−1. Our diffusion data enables us to determine accurate values for the activation enthalpy of diffusion
and the pre-exponential factor. The
= Li, K, Cs and K2O·2BaO·4SiO2 was investigated at temperatures below the respective glass-transition temperatures. The diffusion profiles of the radiotracers were recorded by means of an ion-beam sputtering technique in conjunction with activity measurements. Analysis of the Ca and Ba profiles is based on the thin-film solution of the diffusion equation and a contribution which takes into account the instrumental broadening of the profiles caused by sputtering effects. The diffusion coefficients of the alkaline-earth ions were determined down to values of as low as 10−21 m2 s−1. Our diffusion data enables us to determine accurate values for the activation enthalpy of diffusion
and the pre-exponential factor. The

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...