Themed collection Coronavirus articles - free to access collection

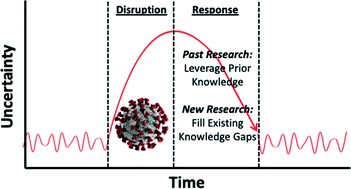
Editorial Perspectives: will SARS-CoV-2 reset public health requirements in the water industry? Integrating lessons of the past and emerging research
Brian Pecson and Daniel Gerrity present an Editorial Perspective which focuses on the impact of SARS-CoV-2 on the water industry.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 1761-1764
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW90031A
Editorial Perspectives: 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): what is its fate in urban water cycle and how can the water research community respond?
Vincenzo Naddeo and Haizhou Liu present an ‘Editorial Perspective’ on coronavirus in wastewater and discuss the water research needs to combat viral outbreaks.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 1213-1216
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW90015J
Rocaglamide and silvestrol: a long story from anti-tumor to anti-coronavirus compounds
The flavagline silvestrol is a potential candidate against viral infections including COVID-19.

Nat. Prod. Rep., 2021,38, 18-23
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NP00024H
Nano- and biosensors for the detection of SARS-CoV-2: challenges and opportunities
Recent advances in the design of nano- and biosensors, as well as important challenges and opportunities related to the detection of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 diagnosis, are discussed.

Mater. Adv., 2020,1, 3092-3103
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MA00702A
The latest strategies in the fight against the COVID-19 pandemic: the role of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles
In this review, we summarize and highlight the latest achievements based on nanoparticles in the fight against COVID-19.
New J. Chem., 2021,45, 6167-6179
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ00047K
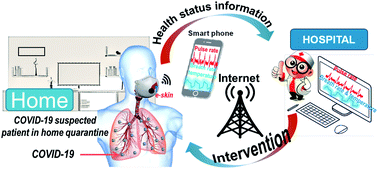
Envisioned strategy for an early intervention in virus-suspected patients through non-invasive piezo- and pyro-electric-based wearable sensors
This perspective explores the scope of piezo- and pyro-electric wearable sensors towards the early intervention of virus-affected patients, particularly in the context of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021,9, 1887-1909
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA08547B
Soft matter science and the COVID-19 pandemic
Much of the science underpinning the global response to the COVID-19 pandemic lies in the soft matter domain.

Soft Matter, 2020,16, 8310-8324
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SM01223H
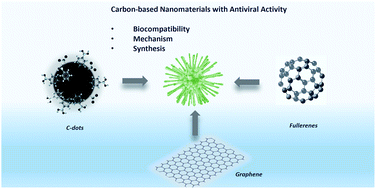
Carbon-based antiviral nanomaterials: graphene, C-dots, and fullerenes. A perspective
The appearance of new and lethal viruses and their potential threat urgently requires innovative antiviral systems.
Chem. Sci., 2020,11, 6606-6622
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SC02658A
Ultraviolet-C and other methods of decontamination of filtering facepiece N-95 respirators during the COVID-19 pandemic
Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation is one method for decontamination of N-95 filtering facepiece respirators to facilitate reuse during the COVID-19 pandemic. Other techniques include hydrogen peroxide vaporization, microwave-generated steaming, and dry heating.
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2020,19, 746-751
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PP00131G
Trends and targets in antiviral phototherapy
With its principles discovered more than a hundred years ago the photodynamic inactivation of viruses is now routinely employed in the decontamination of blood products but also investigated for HPV treatment and water disinfection and food safety.
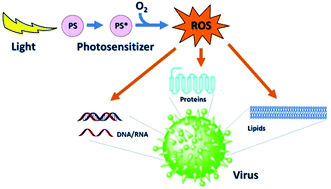
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2019,18, 2565-2612
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9PP00211A
Growth of Legionella during COVID-19 lockdown stagnation
While “avoiding stagnation” has been the mantra of building water experts, support for how this terminology is used is not overly convincing. Carefully nuanced COVID stagnation studies can improve water quality research and communication strategies.
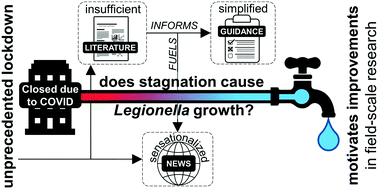
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 10-15
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00819B
Aptamer-based biosensors and their implications in COVID-19 diagnosis
This minireview focusses on the comprehensive study of SARS-CoV-2 specific aptamers and aptamer-based biosensors (optical and electrochemical), and their role and future perspectives in COVID-19 diagnosis.
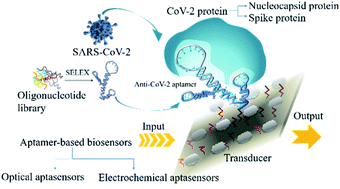
Anal. Methods, 2021,13, 5400-5417
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1AY01519B
Rapid antibody diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 adaptive immune response
The emergence of a pandemic scale respiratory illness (COVID-19) and the lack of the world's readiness to prevent its spread resulted in an unprecedented rise of biomedical diagnostic industries, as they took lead to provide efficient diagnostic solutions for COVID-19.

Anal. Methods, 2021,13, 4019-4037
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1AY00888A
An overview of molecular biology and nanotechnology based analytical methods for the detection of SARS-CoV-2: promising biotools for the rapid diagnosis of COVID-19
Molecular biology and nanotechnology based analytical methods have proven to be promising diagnostic tools for the rapid diagnosis of COVID-19.
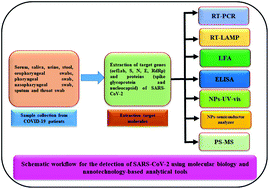
Analyst, 2021,146, 1489-1513
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0AN01528H
The role of biomaterials and three dimensional (3D) in vitro tissue models in fighting against COVID-19
Biomaterials in company with bioengineered tissue models enables scientists to develop the more precise disease models and find better solutions in infectious respiratory disease treatment.
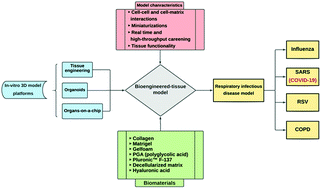
Biomater. Sci., 2021,9, 1217-1226
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0BM01616K
A new point-of-care test for the diagnosis of infectious diseases based on multiplex lateral flow immunoassays
Multiplex lateral flow immunoassays for outstanding POCT of infectious diseases.
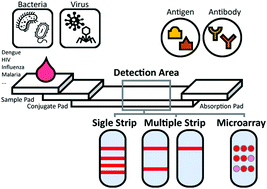
Analyst, 2019,144, 2460-2466
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AN02295J
Novel biosensing methodologies for ultrasensitive detection of viruses
Biosensors function as rapid, sensitive and specific diagnostic tools for various viral infectious diseases.
Analyst, 2013,138, 6219-6229
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN01394D
Anti-tumor, -viral, and -bacterial activities of polyoxometalates for realizing an inorganic drug
Recent developments in the biological activities of polyoxometalates (metal-oxide cluster anions) are discussed from the chemotherapeutic point of view for a novel inorganic drug.
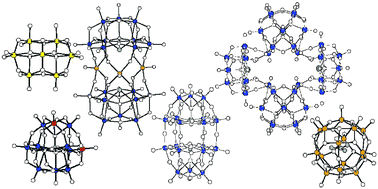
J. Mater. Chem., 2005,15, 4773-4782
https://doi.org/10.1039/B504585A
Development of nanozymes for promising alleviation of COVID-19-associated arthritis
Nanozymes, with functions such as virus disinfection, oxidative stress reduction, cytokine production regulation, and inflammation reduction, may be a promising treatment for COVID-19-related arthritis linked to shared factors.
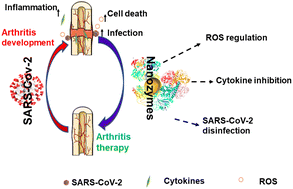
Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 5781-5796
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00095H
Computational methods directed towards drug repurposing for COVID-19: advantages and limitations
Different kind of methods utilized in expediting drug repurposing.

RSC Adv., 2021,11, 36181-36198
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA05320E
A nano perspective behind the COVID-19 pandemic
Nano-scale interactions are key to understand the SARS-CoV-2 infectious potential and bio–nano sciences can provide hints on viral particles behaviour.
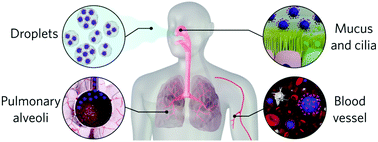
Nanoscale Horiz., 2021,6, 842-855
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NH00135C
A critical overview of computational approaches employed for COVID-19 drug discovery
We cover diverse methodologies, computational approaches, and case studies illustrating the ongoing efforts to develop viable drug candidates for treatment of COVID-19.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021,50, 9121-9151
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CS01065K
Nanomaterial-based drug delivery systems as promising carriers for patients with COVID-19
We propose a consideration of Avigan-loaded nano-emulsions as a promising nano-based delivery system for the treatment of COVID-19.
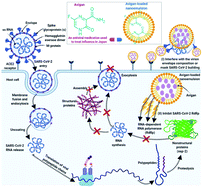
RSC Adv., 2021,11, 26463-26480
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA04835J
A review of the latest research on Mpro targeting SARS-COV inhibitors
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, the pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection is still spreading at an alarming rate and has caused huge loss of life and economic damage worldwide.

RSC Med. Chem., 2021,12, 1026-1036
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MD00066G
A comprehensive overview of vaccines developed for pandemic viral pathogens over the past two decades including those in clinical trials for the current novel SARS-CoV-2
We describe updated information on the various vaccines available over the last two decades, along with recent progress in developing 63 diverse vaccines against SARS-CoV-2.
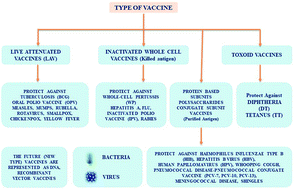
RSC Adv., 2021,11, 20006-20035
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA09668G
A review on potential of natural products in the management of COVID-19
In this review promising targets for drug development against SARS-CoV-2 and anti-viral activities of some of the known natural products (including plant secondary metabolites) are discussed.
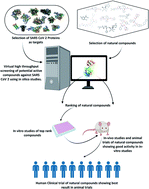
RSC Adv., 2021,11, 16711-16735
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA00644D
SARS-CoV-2 and tissue damage: current insights and biomaterial-based therapeutic strategies
Schematic representation of use of biomaterials in tissue regeneration for SARS-CoV-2-affected organs.
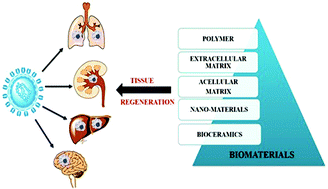
Biomater. Sci., 2021,9, 2804-2824
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0BM02077J
Targeting the SARS-CoV-2-spike protein: from antibodies to miniproteins and peptides
Fighting COVID-19 with high affinity reagents: this review article summarizes the discovery of several classes of (bio) molecules targeting the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
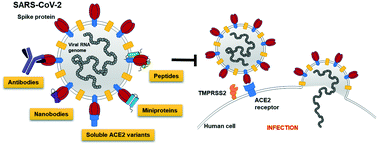
RSC Med. Chem., 2021,12, 197-202
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MD00385A
The chemical biology of coronavirus host–cell interactions
Chemical biology strategies can play important roles in studying the complexity of SARS-CoV-2–host interactions at molecular level detail.

RSC Chem. Biol., 2021,2, 30-46
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00197J
ACE2 as a potential therapeutic target for pandemic COVID-19
SARS-CoV-2 virus invades the host through angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors by decreasing the ACE2 expression of the host.

RSC Adv., 2020,10, 39808-39813
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA08228G
Diagnostic technologies for COVID-19: a review
Summary of the latest research progress on detection methods of SARS-CoV-2, providing a reference to develop rapid and accurate diagnostic strategies for COVID-19.
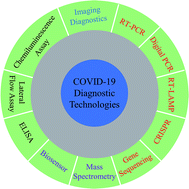
RSC Adv., 2020,10, 35257-35264
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA06445A
Targeting severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus (SARS-CoV-1) with structurally diverse inhibitors: a comprehensive review
Since the coronaviruses that cause COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-1 share 80% structural similarity, we present a comprehensive review of the diverse molecular inhibitors of SARS-CoV-1. This will help to accelerate drug discovery for deadly coronavirus diseases.
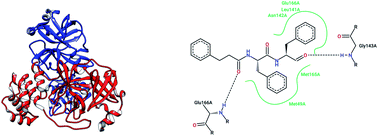
RSC Adv., 2020,10, 28287-28299
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA04395H
An overview of key potential therapeutic strategies for combat in the COVID-19 battle
A schematic representation of different methods to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection.
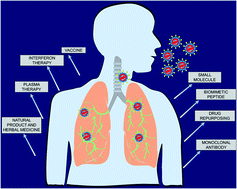
RSC Adv., 2020,10, 28243-28266
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA05434H
Potential repurposed SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection drugs
The global outbreak of COVID-19 viral infection is associated with the absence of specific drug(s) for fighting this viral infection.
RSC Adv., 2020,10, 26895-26916
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA05821A
Nature as a treasure trove of potential anti-SARS-CoV drug leads: a structural/mechanistic rationale
Potential drug candidates derived from natural sources are posed for the development of anti-SARS CoV-2 therapeutics.
RSC Adv., 2020,10, 19790-19802
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA04199H
In search for effective and definitive treatment of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) infections
Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 (HSV-1) is a nuclear replicating enveloped virus.
RSC Adv., 2016,6, 1058-1075
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA22896D
Antiviral drug discovery: broad-spectrum drugs from nature
Exploiting the power of nature to fight viral infections. This review describes the concept of direct- and host-acting natural products with broad-spectrum antiviral activities and provides promising examples derived from plants, fungi, bacteria and marine organisms.
Nat. Prod. Rep., 2015,32, 29-48
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NP00085D
Influenza neuraminidase: A druggable target for natural products
This review covers the increasing research efforts of the past decade, focusing on the structure, function and druggability of influenza NA, and its inhibition by natural products. Latest developments in theoretical and experimental research on NA for lead discovery strategies from nature are presented.
Nat. Prod. Rep., 2012,29, 11-36
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1NP00053E
Molecular diagnostics in the era of COVID-19
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to escalate globally and acquires new mutations, accurate diagnostic technologies continue to play a vital role in controlling and understanding the epidemiology of this disease.
Anal. Methods, 2021,13, 3744-3763
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1AY00947H
Point-of-care testing detection methods for COVID-19
This paper summarises the latest research advances and commercial products in POCT-based SARS-CoV-2 detection methods.
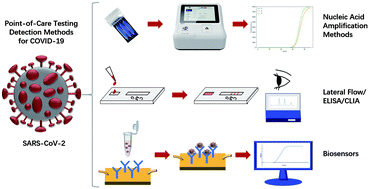
Lab Chip, 2021,21, 1634-1660
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0LC01156H
A review of pharmaceutical occurrence and pathways in the aquatic environment in the context of a changing climate and the COVID-19 pandemic
Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are increasingly being identified as contaminants of emerging concern (CECs).
Anal. Methods, 2021,13, 575-594
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0AY02098B
Current advances in the detection of COVID-19 and evaluation of the humoral response
SARS-CoV-2 and humoral response determinations to understand and control the spread of COVID-19.
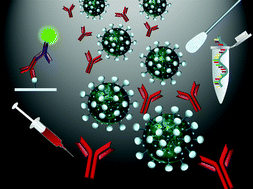
Analyst, 2021,146, 382-402
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0AN01686A
Detection of RNA viruses from influenza and HIV to Ebola and SARS-CoV-2: a review
RNA-based viruses likely make up the highest pandemic threat among all known pathogens in about the last 100 years, since the Spanish Flu of 1918 with 50 M deaths up to COVID-19.
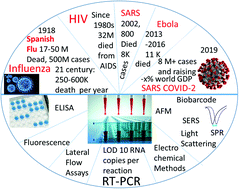
Anal. Methods, 2021,13, 34-55
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0AY01886D
Emerging investigators series: the source and fate of pandemic viruses in the urban water cycle
This review provides a comprehensive look at whether a pandemic enveloped virus would pose challenges for the wastewater and drinking water industries.
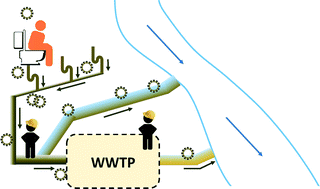
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2015,1, 735-746
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EW00125K
The role of biosensors in the detection of emerging infectious diseases
An ideal approach to real-time disease detection and surveillance.
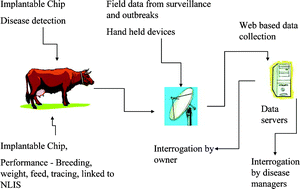
Analyst, 2006,131, 1079-1090
https://doi.org/10.1039/B603402K
Site-specific recognition of SARS-CoV-2 nsp1 protein with a tailored titanium dioxide nanoparticle – elucidation of the complex structure using NMR data and theoretical calculation
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles can be tailored to interact specifically with SARS-CoV-2 nsp1 protein, forming, according to NMR studies, a stable complex, which structure was elucidated based on a molecular modeling approach.
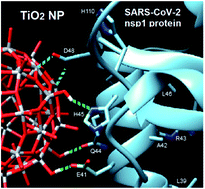
Nanoscale Adv., 2022,4, 1527-1532
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NA00855B
Uncovering mechanisms of RT-LAMP colorimetric SARS-CoV-2 detection to improve assay reliability
In this study, we enhanced the color changes and sensitivity of colorimetric SARS-CoV-2 RT-LAMP assays based on triarylmethane dyes. We determined a mechanism for the color changes and obtained sensitivities of 10 RNA copies per microliter.
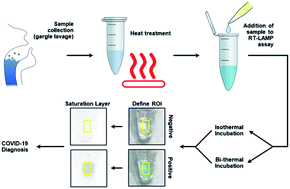
Anal. Methods, 2022,14, 378-382
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1AY01395E
An electrochemical SARS-CoV-2 biosensor inspired by glucose test strip manufacturing processes
A rapid, low cost sensor for Covid-19 was developed using a perfluorodecanthiol layer and ACE2.
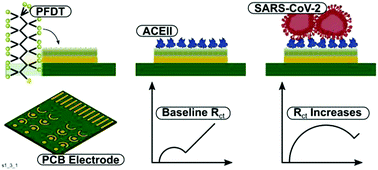
Chem. Commun., 2021,57, 3704-3707
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CC00936B
Colorimetric loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for cost-effective and quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2: the change in color in LAMP-based assays quantitatively correlates with viral copy number
Colorimetric LAMP for COVID-19 intensified diagnostics: a simple and quantitative method comparable in diagnostic performance to RT-qPCR.
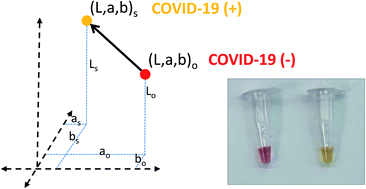
Anal. Methods, 2021,13, 169-178
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0AY01658F
High-throughput wastewater analysis for substance use assessment in central New York during the COVID-19 pandemic
Wastewater analysis provides insights into population lifestyle and health status during the coronavirus pandemic.
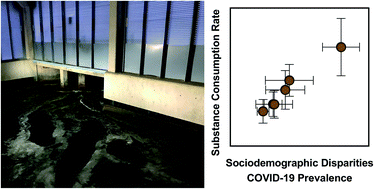
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 2147-2161
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EM00377H
Inhibitory activities of marine sulfated polysaccharides against SARS-CoV-2
Sulfated polysaccharide from sea cucumber (SCSP), fucoidan from brown algae, and iota-carrageenan from red algae show inhibitory activities against SARS-CoV-2.
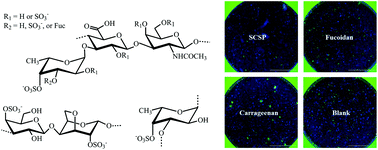
Food Funct., 2020,11, 7415-7420
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0FO02017F
Paper spray mass spectrometry utilizing Teslin® substrate for rapid detection of lipid metabolite changes during COVID-19 infection
Development of an identification methodology with PS-MS as a sensitive and rapid technique to obtain vastly different chemical changes in COVID-19 infection.
Analyst, 2020,145, 5725-5732
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0AN01074J
Quantitative determination of mechanical stability in the novel coronavirus spike protein
Unveiling the nanomechanical stability of the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein
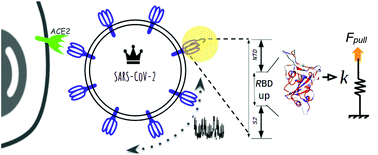
Nanoscale, 2020,12, 16409-16413
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR03969A
Interaction of hydroxychloroquine with SARS-CoV2 functional proteins using all-atoms non-equilibrium alchemical simulations
Using a combination of enhanced sampling molecular dynamics techniques and non-equilibrium alchemical transformations, we have shown that hydroxychloroquine may act as a mild inhibitor of important functional proteins for SARS-CoV2 replication.
Chem. Commun., 2020,56, 8854-8856
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CC03558K
MPLEx: a method for simultaneous pathogen inactivation and extraction of samples for multi-omics profiling
The continued emergence and spread of infectious agents is of great concern, and systems biology approaches to infectious disease research can advance our understanding of host–pathogen relationships and facilitate the development of new therapies and vaccines.
Analyst, 2017,142, 442-448
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AN02486F
Multicolored silver nanoparticles for multiplexed disease diagnostics: distinguishing dengue, yellow fever, and Ebola viruses
Multicolor silver nanoparticles enable multiplexed detection of dengue, yellow fever, and Ebola virus proteins in a single lateral flow strip.
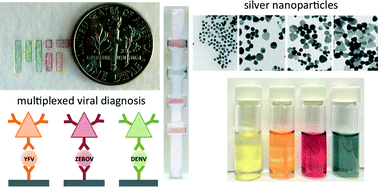
Lab Chip, 2015,15, 1638-1641
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5LC00055F
Inhibition of SARS coronavirus helicase by bismuth complexes
The SARS-CoV NTPase/helicase being able to unwind both RNA and DNA duplexes, is an attractive target for anti-viral drug design. A series of bismuth complexes were synthesized and characterized, and exhibit the inhibition against the SARS helicase ATPase and duplex-unwinding activities at micromolar concentrations.
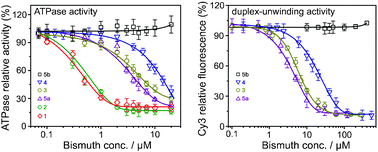
Chem. Commun., 2007, 4413-4415
https://doi.org/10.1039/B709515E
Determination of intermediate state structures in the opening pathway of SARS-CoV-2 spike using cryo-electron microscopy
A structural ensemble derived from cryo-electron microscopy reveals a cryptic pocket site in intermediate states along the opening pathway of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
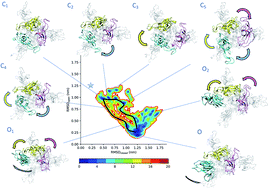
Chem. Sci., 2021,12, 9168-9175
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC00244A
Translating daily COVID-19 screening into a simple glucose test: a proof of concept study
COVID-19 glucose test: translating SARS-CoV-2 detection into a glucose test is achieved by incorporating target-responsive rolling circle amplification and a CRISPR-based collateral cleavage module with a portable glucose meter.
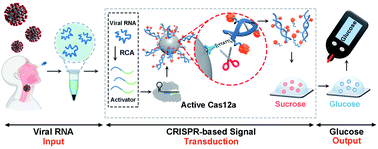
Chem. Sci., 2021,12, 9022-9030
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC00512J
Prediction and mitigation of mutation threats to COVID-19 vaccines and antibody therapies
Antibody therapeutics and vaccines are among our last resort to end the raging COVID-19 pandemic.

Chem. Sci., 2021,12, 6929-6948
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC01203G
Molecular recognition of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein: quantum chemical hot spot and epitope analyses
Quantum chemical calculations investigated molecular recognition of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoproteins including its N501Y variant for ACE2 and antibody. Hot spot and epitope analyses revealed key residues to design drugs and antibodies against COVID-19.
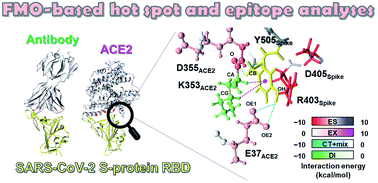
Chem. Sci., 2021,12, 4722-4739
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SC06528E
High-resolution mining of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease conformational space: supercomputer-driven unsupervised adaptive sampling
We provide an unsupervised adaptive sampling strategy capable of producing μs-timescale molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of large biosystems using many-body polarizable force fields (PFFs).
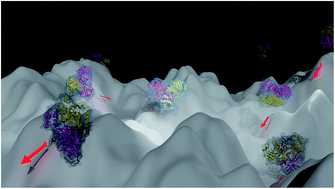
Chem. Sci., 2021,12, 4889-4907
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC00145K
A microscopic description of SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibition with Michael acceptors. Strategies for improving inhibitor design
Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease by a Michael acceptor is studied using classical and QM/MM simulations. Results point out to a transition state with a key water molecule stabilizing the catalytic dyad and assisting the protonation step.

Chem. Sci., 2021,12, 3489-3496
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SC04978F
Mechanism of inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro by N3 peptidyl Michael acceptor explained by QM/MM simulations and design of new derivatives with tunable chemical reactivity
QM/MM simulations identify the mechanism of reaction of N3, a covalent peptidyl inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Modelling of two novel proposed compounds, B1 and B2, suggests that reversibility of covalent inhibition could be tailored.
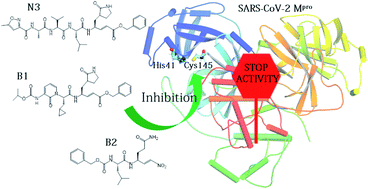
Chem. Sci., 2021,12, 1433-1444
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SC06195F
Inhibitor binding influences the protonation states of histidines in SARS-CoV-2 main protease
The main protease (Mpro) of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is an attractive target for antiviral therapeutics.
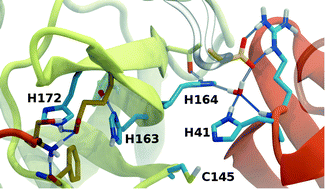
Chem. Sci., 2021,12, 1513-1527
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SC04942E
Probing conformational hotspots for the recognition and intervention of protein complexes by lysine reactivity profiling
A mass spectrometry-based two-step isotope labeling-lysine reactivity profiling strategy is developed to probe the molecular details of protein–protein interactions and evaluate the conformational interventions by small-molecule active compounds.
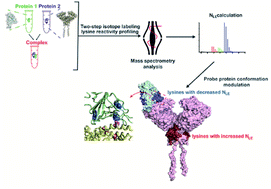
Chem. Sci., 2021,12, 1451-1457
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SC05330A
Molecular mechanism of inhibiting the SARS-CoV-2 cell entry facilitator TMPRSS2 with camostat and nafamostat
The authors unravel the molecular action principle of nafamostat and camostat, two potential COVID-19 drugs targeting the human protein TMPRSS2.

Chem. Sci., 2021,12, 983-992
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SC05064D
Inhibitors of thiol-mediated uptake
Thiol-reactive inhibitors for the cellular entry of cyclic oligochalcogenide (COC) transporters and SARS-CoV-2 spike pseudo-lentivirus are reported.

Chem. Sci., 2021,12, 626-631
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SC05447J
A serological aptamer-assisted proximity ligation assay for COVID-19 diagnosis and seeking neutralizing aptamers
A versatile aptamer-assisted proximity ligation system improves diagnosis of COVID-19, and allows the evaluation of potential neutralizing aptamers.
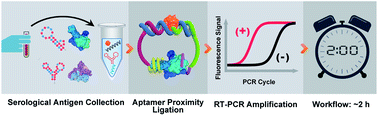
Chem. Sci., 2020,11, 12157-12164
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SC03920A
Unveiling the molecular mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibition from 137 crystal structures using algebraic topology and deep learning
By integrating algebraic topology and deep learning, we provide a reliable ranking of binding affinities, binding site analysis, and fragment decomposition for 137 SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors.
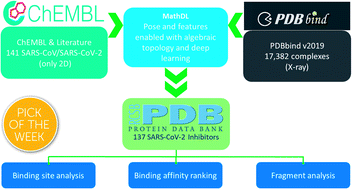
Chem. Sci., 2020,11, 12036-12046
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SC04641H
About this collection
All Royal Society of Chemistry articles on coronavirus research can be found here and are free to access.