Astilbin attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway
Abstract
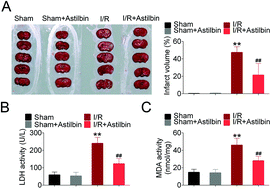
Ischemic stroke is the second most common cause of death worldwide and cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury also leads to serious tissue damage. Astilbin, a natural bioactive flavonoid compound, has been reported to have protective effects on neurological diseases. This study aims to investigate the effects of astilbin on cerebral I/R injury and determine the mechanisms involved. The results demonstrated that, in cerebral I/R rats, astilbin could attenuate I/R injury in the hippocampal region, decreasing the activity of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and malondialdehyde (MDA) in the rat brain. Astilbin also inhibited the I/R-induced upregulation of pro-inflammatory mediators (TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6). Similarly, in hypoxia/reperfusion (H/R) treated human neuroblastoma cells, astilbin could increase the cell viability of SH-SY5Y, decrease the activity of LDH and MDA, and inhibit the H/R-induced upregulation of pro-inflammatory mediators. For the mechanism study, western blot results indicated that astilbin could inhibit the expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), myeloid differential protein 88 (MYD88) and phosphorylated NF-κB p65 in H/R treated SH-SY5Y cells. The research indicated that astilbin ameliorated cerebral I/R injury partly via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Astilbin may have potential therapeutic effects on cerebral ischemia.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...