Arsenic aggravated reproductive toxicity in male rats exposed to lead during the perinatal period
Abstract
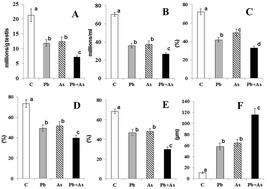
The aim of this study was to assess the reproductive toxic effects of arsenic on adult Wistar rats exposed to lead during the perinatal period. The pregnant rats were allowed ad libitum access to tap water containing 819 mg of lead (Pb) per L or without Pb from conception until weaning. Litter size, survival rate and developmental milestones of the pups delivered by Pb exposed dams were comparable to those of the control rats. Conversely, the pups exposed to Pb during the perinatal period exhibited significant delay in cliff avoidance, negative geotaxis, surface righting reflex, ascending wire mesh and testis descent. The control and perinatal Pb-exposed male rats were maintained on tap water containing 2.3 mg of arsenite (As) per L or without arsenite from the pubertal period (post-natal day 55) to adulthood (post-natal day 115) and assessed for reproductive end points. The results revealed that the (1) relative weights of the testis, epididymis, seminiferous tubules and ventral prostate; (2) daily sperm production; (3) epididymal sperm density and (4) numbers of motile, viable, and HOS tail swelled sperm declined significantly in the rats exposed to either Pb or As. The activity levels of testicular 3β- and 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases were also significantly decreased in the experimental rats. Significant elevation in the levels of reactive oxygen species and lipid peroxidation in association with reduced activities of antioxidant enzymes in the testis and different epididymal regions was recorded in the experimental rats. In the fertility study, although each male in the control and experimental groups produced a copulatory plug and impregnated a female, the mean conception time significantly increased in the experimental groups. The mean number of implantations decreased significantly in the females mated with the experimental males. Moreover, the results of the present study also indicate that reproductive alterations were more deteriorated in the Pb-exposed rats treated with arsenic when compared to individual exposures. In conclusion, the data clearly suggest that reproductive toxicity in male rats exposed to Pb during the perinatal period is exacerbated by As treatment during the pubertal period.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...