Strategy of metal iron doping and green-mediated ZnO nanoparticles: dissolubility, antibacterial and cytotoxic traits†
Abstract
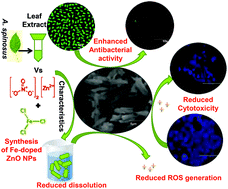
Undoped and Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) were synthesized using Amaranthus spinosus leaf extract as a reducing agent. The physicochemical traits, dissolution, cytotoxicity, as well as the antioxidant, photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of synthesized NPs were investigated. The results revealed that ZnO NPs were rod shaped with hexagonal phase structure, and their crystal size, dissolubility and aggregation decreased with Fe doping of NPs. Cytotoxicity of the NPs was studied against MCF-7 cells by MTT assay. IC50 values for undoped and 1 wt% Fe-doped ZnO NPs were found to be 400 and 600 μg mL−1, respectively. Cell viability with Fe-doped ZnO NPs was higher than with undoped ZnO. Among the synthesized NPs, A. spinosus-mediated 1 wt% Fe-doped ZnO shows a better decolourization efficiency of 97% for indigo carmine dye under solar irradiance. The antibacterial activity of NPs was tested against Gram-negative Escherichia coli and Gram-positive Bacillus safensis using disc diffusion, minimum inhibitory concentration and growth curve method. The bactericidal activity of Fe-doped ZnO NPs was more prominent with E. coli than B. safensis bacteria and when compared to undoped ZnO.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...