Recent advances on the bacterial cellulose-derived carbon aerogels
Abstract
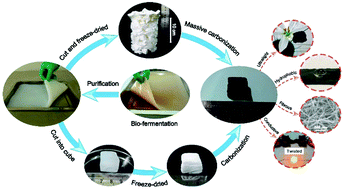
Bacterial cellulose (BC), sustainable biomass, has long been envisioned as a fantastic biomass material since it was discovered by Brown in 1886. BC cultivated in static medium appears as a never-dried hydrogel, wherein numerous nanofibers are highly interconnected, building into a three-dimensional (3D) architecture. Although BC has achieved great success in the area of biological medicine, the electronic inertness and susceptible bio-invasion restrict its further applications demanding electronic migration and durability. Carbonization has been employed to endow BC with superior conductivity and chemical tolerance without destroying the 3D architecture. Moreover, carbonized BC (CBC) exhibits exceptional properties such as ultralightweight, high surface area, good volumetric resilience, and superhydrophobicity, which are necessary for electrochemical energy, microwave attenuation, and selective absorption. The industrial production of BC facilitates the massive fabrication of high value-added CBC with low-cost precursors. This review summarizes the latest developments on the CBC-based functional materials, including state-of-the-art design concepts and synthetic strategies. Our prospects on the major obstacles in the approach of further exploitation of CBC, as well as the promising avenues in front of these issues are proposed in this review.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry C Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...