In situ assembly of a wearable capacitive sensor with a spine-shaped dielectric for shear-pressure monitoring†
Abstract
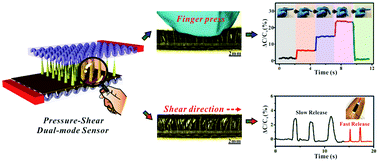
Recently, flexible devices that can implement both pressure and shear force monitoring have attracted abundant interest. Even though flexible sensors with optimized pressure monitoring have been widely explored, the shear branch is yet to be fully addressed as it is restricted by the device assembly and structural features. Herein, we present the magnetic field-assisted in situ formation of spine arrays as the dielectric layer for a capacitive sensor that can respond to both normal pressure and shear force. The template-free and facile approach can not only induce a spine-shaped dielectric as a highly compressible medium for pressure sensing but can also simultaneously realize the device assembly for sustainable shear force monitoring. The capacitive sensor exhibits sensitive pressure monitoring with a detection limit of 2 Pa and possesses reliable and recoverable shear perception with a sensitivity of 0.0752 N−1 (0.015–0.50 N) and 0.0177 N−1 (0.50–1.30 N). As a proof of concept, the device was applied as a wearable motion indicator, artificial intelligence, and body force sensor in terms of pressure and shear force recognition. We believe that the demonstrated methodology can be promising for future wearable electronics thanks to the advantages such as facile production, competitive detection performance, and capability of pressure-shear monitoring.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...