Facile green synthesis of ZnInS quantum dots: temporal evolution of their optical properties and cell viability against normal and cancerous cells
Abstract
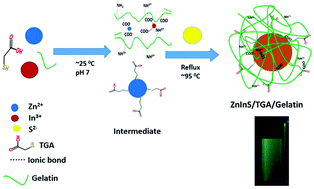
The inherent heavy metal toxicity of fluorescent binary quantum dots (QDs) despite their excellent optical properties has limited their biological applications. This has shifted the research focus towards toxic-metal free chalcopyrite ternary QDs such as AgInS2 (AIS), CuInS2 (CIS), ZnInS (ZIS) QDs etc. Among these QDs, ZIS has been given less attention irrespective of its advantages over other conventional ternary QDs. This is attributed to the difficulty in producing zero dimensional (0D) ZIS via an aqueous synthetic route compared to other morphologies. We herein report the facile and ecofriendly aqueous synthesis, properties and cellular activity of 0D ZIS. The synthesis was carried out via a reflux method using thioglycolic acid (TGA) and gelatin as a capping ligand and a stabilizer. The temporal evolution of the optical properties was investigated by varying the pH, TGA concentration, amount of gelatin, Zn/In ratio and sulfur concentration. The as-synthesized QDs show narrow emission, with pH, TGA concentration and sulfur concentration showing a great influence on the emission intensity. The optimized parameters for better fluorescence was obtained at pH = 7, 21.5 mmol of TGA and Zn : In ratio = 1 : 4. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images showed that the as-synthesised ZIS QDs are small, monodispersed, crystalline and spherical in shape with an average particle size of 3 nm while Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra confirmed the capping of ZIS QDs by TGA and gelatin. The as-synthesized QDs are highly stable with excellent biocompatibility towards normal cells (BHK-21) and cancerous cells (HeLa) even at high concentration (1000 μg mL−1).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...