Topological tailoring of structure and defects to enhance red to near-infrared afterglow from Mn2+-doped germanate photonic glasses†
Abstract
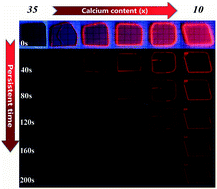
The generation of optical afterglow and comprehension of the structure–function mechanism in glasses have not been well studied to date owing to the uncertainty of internal structure and defects, let alone being able to tailor the afterglow. Herein, we fabricate a new type of Mn2+-doped calcium aluminium germanate photonic glasses that demonstrate red to near-infrared persistent luminescence from 560 to 820 nm. Provoked by the understanding of amorphous structure continuity, facile network topology was utilized as a tuning strategy, resulting in modulation of the persistent luminescence time from 30 min to longer than 24 h. The density of correlative electronic defects increases with their depth gradually deepening from 0.69, 0.78, and 0.83 eV to 0.80, 0.85, and 0.90 eV. Multiple measurements reveal that the internal structure evolves towards regular crosslinking, promoting the incorporation and stabilization of Mn2+ along with the change of defects, all of which are conducive to afterglow. The possible attribution of defects stems not only from the structural intrinsic state, but also from defects caused by the photo-oxidation of Mn2+. Coupled with their association to afterglow, the mechanism of persistence regulation is expounded in detail, and its potential applications in displays and in vivo imaging are demonstrated. This work suggests accessible references to the rational design of persistent materials with flexible persistence or even other advantageous functions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...