Flexible metal–organic frameworks for the wavelength-based luminescence sensing of aqueous pH†
Abstract
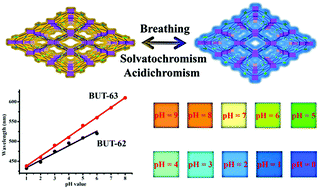
Luminescence sensing is commonly based on the change of emission intensity, lifetime, and/or quantum yield of luminescent materials. Wavelength-based luminescence sensing has been comparatively rarely documented. Flexible metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) with rich fluorophores are promising sensory materials due to their unique stimuli-responsive luminescence. However, it is still challenging to construct such materials with high hydrolytic stability, which would allow them to be utilized in water systems. Here, we present two isoreticular flexible MOFs synthesized by carbazole-derived ligands, which show high porosity and excellent stability in aqueous solutions with a wide range of pH values. Interestingly, both MOFs show a structural breathing behavior with variation of the guest molecules inside their pores due to the topologically allowed flexibility. With their frameworks breathing, sensitive fluorescence changes in the wavelength of the maximum emission have been observed. Remarkably, the wavelengths of the maximum emission are well dependent on the pH values (1 to 8) of the aqueous solution in a linear relationship, suggesting a new means of accomplishing pH sensing based on emission wavelength instead of intensity. Wavelength-based fluorescence sensing thus offers an alternative way of achieving pH indication, free from some of the drawbacks associated with intensity-based fluorescence sensing, which should be fundamentally important for the development of new pH sensors in environmental and life sciences.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...