A highly sensitive and stable SERS substrate using hybrid tungsten dioxide/carbon ultrathin nanowire beams†
Abstract
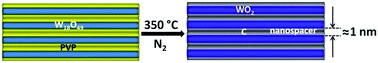
Compared to noble metals, semiconductor surface enhanced Raman spectrum (SERS) substrates are much cheaper, but their poor sensitivity and stability limits their applications. Here, we report a remarkable enhancement of Raman signals observed from hybrid WO2/C ultrathin nanowire beams. An outstanding enhancement factor (EF) of 1.3 × 106 is achieved, and the lowest detection limit is up to 10−8 M. More importantly, the new SERS active substrate shows ultrahigh chemical, thermal, and light stabilities. An electromagnetic enhancement model and an interfacial charge transfer model coexist in the new SERS substrate.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...