An elastomer for epidermal electronics with adjustable adhesion force and stretchability obtained via a reverse-micelle-induced process†
Abstract
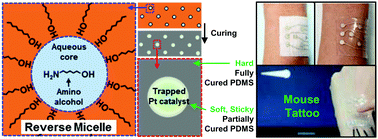
A reverse-micelle-induced process for the filler–matrix composites proposed in this study can form and arrange the spots where the fillers are locally concentrated in the composite. By adjusting the filler concentration and degree of arrangement, a novel material can be obtained which cannot be achieved with conventional uniformly dispersed composites. Through the process, the reverse-micelle can envelop and deliver the hydrophilic filler into the hydrophobic polymer matrix. The size and the degree of the arrangement of the reverse-micelle are easily adjustable, so the enveloped filler is also adjustable. To demonstrate this method, we made an elastomer essential for epidermal devices. The degrees of stretchability, softness, stickiness, and durability of the elastomer demanded by each application of epidermal electronic devices vary widely. Moreover, the weak link of polymer chains required for stretchability and stickiness also makes the material weaker, making it difficult to obtain suitable materials. This study solves this problem by locally forming weakly linked regions in a polydimethylsiloxane-based elastomer. The method can readily control and extend the range of the properties, adhesion force (0.014–1.1 N cm−1), Young's modulus (16–535 kPa), and stretchability (430–1340%). Further, the elastomer exhibits excellent durability (stable up to 10 000 stretching cycles at 100% strain), and is reusable, and adheres well to human skin. Even when the skin is wet, the adhesion force is maintained at 80%. These features allowed us to create an attachable patch with a function of the computer mouse that could be recycled rather than disposable. This method will help researchers make elastomers suitable for their applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...