One-dimensional aluminum nanoparticle chains: the influence of interparticle spacing and chain length on plasmon coupling behavior†
Abstract
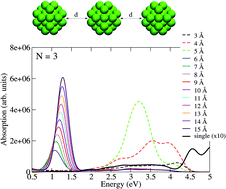
Ordered arrangements of metal nanoparticles have attracted significant interest due to their ability to focus and confine light to deeply subwavelength scales. We used time dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) calculations to investigate the plasmon coupling behavior of one-dimensional aluminum (Al) nanoparticle chains. Although individual Al nanoparticles absorb strongly in the ultraviolet (UV) region, the collective interaction between chains of nanoparticles creates strongly tunable near infrared (NIR) gap plasmon resonances. The chains are composed of 3 to 7 nanoparticles with interparticle distances (d) varying from 3 to 15 Å. We observe progressive redshifting of the NIR gap plasmon and systematic spectral amplitude reduction with decreasing d in the range of 6 to 15 Å, which is independent of the chain length (N). The spectral amplitudes and absorption cross sections for different chains with identical d values are substantially modulated with increasing N, indicating that the dipole moment of the system is enhanced. As d is further reduced to 5 Å, the redshifting gap plasmon is replaced by a blueshifting charge-transfer plasmon. This result should motivate a better understanding of Al supermolecules and the creation of ordered arrangements of Al nanoclusters for various applications ranging from chemical sensing to catalysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...