Monitoring emulsion microstructure by using organic electrochemical transistors†
Abstract
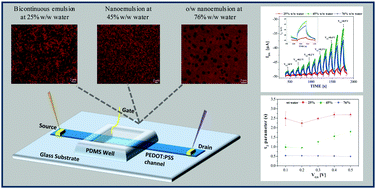
Organic electrochemical transistors (OECTs) are powerful amplifying transducers of chemical signals allowing us to measure ionic transport between an electrolyte solution and an organic semiconductor film with nanosensing capabilities and low cost of fabrication. Here, we report how OECTs can also be exploited to detect microstructural features of complex soft materials, such as oil/water emulsions. To this purpose, the response of OECTs is investigated for samples obtained at different stages of a nano-emulsification process carried out by gradually adding water to a mixture of oil and two non-ionic surfactants. Our results demonstrate that, above a critical water volume fraction, OECTs are able to work as depletion-mode transistors displaying specific features in terms of the final current modulation capability and the transient time response. In particular, the kinetics of the device current upon the application of step-like probing gate voltages is successfully modelled by using a double exponential law with characteristic time constants. We relate the OECT behavior to the clustering and percolation of water droplets as detected by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) and rheometrical measurements. Our results lay the foundation for the quantitative application of OECTs to identify the phase behaviour and microstructure in complex soft materials, a relevant issue in industrial processing and material characterization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...