Synthesis of colloidal MnSb nanoparticles: consequences of size and surface characteristics on magnetic properties†
Abstract
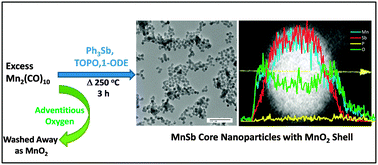
A solution phase methodology was developed for the formation of discrete colloidal MnSb nanoparticles using dimanganesedecacarbonyl and triphenylantimony as the main reaction components. Stoichiometric reactions result in significant Sb impurities, but these can be eliminated by the use of excess Mn reagent, limiting the reaction time, and using a lower temperature (280 °C) relative to that commonly employed for MnP or MnAs synthesis (330–360 °C). The resultant MnSb nanoparticles are, when evidenced by both powder X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy, ca. 14 nm in diameter and exhibit low polydispersity (13 ± 1.7 nm). High Angle Annular Dark Field-Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy and energy dispersive line scan data revealed that the as-synthesized MnSb nanoparticles are core–shell in nature, having a MnSb core and an amorphous manganese oxide shell. Evidence is presented supporting a pathway for decomposition of MnSb nanoparticles driven by formation of MnO2 and Sb due to reaction with adventitious O2. The MnSb nanoparticles are superparamagnetic at room temperature, and exhibit suppressed moments attributed to surface oxidation arising from the high surface area and intrinsic oxophilicity of Mn.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...