Non-laminated growth of chlorine-doped zinc oxide films by atomic layer deposition at low temperatures†
Abstract
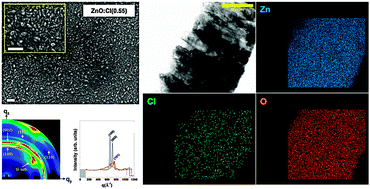
Chlorine doping in a ZnO matrix to a concentration of 0.65 ± 0.05 at% was accomplished via atomic layer deposition using a home-made chlorine source at a low deposition temperature of 140 °C. Structural and morphological properties were investigated using X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy, and grazing incidence wide-angle X-ray diffraction. The introduction of chlorine into the ZnO matrix resulted in significant grain growth reorientation due to chlorine doping in the oxygen sites of ZnO. Cl− ions preferentially occupied the substitutional O− ion site and O vacancies, and the preferential growth in the {100} planes changed to growth in the {002} planes along the longitudinal direction of the hexagonal wurtzite structure as a function of the Cl doping levels. This important phenomenon was explained by a passivation effect, resulting from the chlorine doping mechanism; this was elucidated using transmission electron microscopy. The optical transmittances of the undoped ZnO and ZnO:Cl films were approximately the same (88%), but the optical band gap was increased by the introduction of a Cl dopant in ZnO due to the Burstein–Moss effect. The lowest resistivity of ZnO:Cl was 1.215 × 10−2 Ω cm, and the corresponding carrier concentration and mobility were 5.715 × 1019 cm−3 and 31.81 cm2 V−1 s−1, respectively. Finally, the calculated doping efficiency of chlorine in ZnO was 10.8%, which was higher than that of aluminum-doped ZnO, even though the deposition temperature was very low when applied to plastic substrates due to the non-laminated growth of ZnO:Cl films.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...