Effects of proton irradiation on Si-nanocrystal/SiO2 multilayers: study of photoluminescence and first-principles calculations†
Abstract
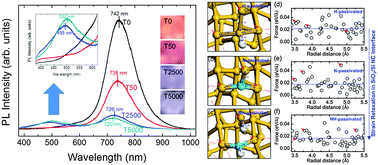
Si nanocrystal (NC)/SiO2 multilayers containing interfacial nitrogens are formed by radiofrequency magnetron-sputtering and post-annealing. By analyzing the photoluminescence (PL) of the multilayer structures after proton irradiation (PI), we found that the peak at ∼740 nm was shifted toward shorter wavelengths and that its intensity was considerably suppressed. Furthermore, a new peak simultaneously appeared at ∼500 nm. We interpret that PI not only modifies the shapes of the Si NCs and generate defects at the NC/SiO2 interface, but also induces simultaneously hydrogen passivation (HP) of interfacial nitrogens due to the attenuated protons. To investigate the relationship between the HP of N at the Si NC/SiO2 interface and the observed band gap reduction of Si NC structures within the SiO2 matrix, we modeled the atomic configurations at the interface and applied first-principles calculations. The results clearly indicate that the HP of composite structures containing Si–N bonds at the Si NC/SiO2 interface induces the blue-shift in PL. We expect that this investigation helps to pave the way for developing more efficient Si-based light emitting devices or solar cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...