Achieving efficient Tb3+ dual-mode luminescence via Gd-sublattice-mediated energy migration in a NaGdF4 core–shell nanoarchitecture†
Abstract
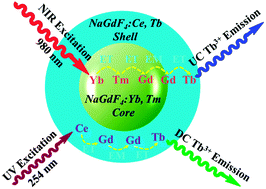
A strategy to realize dual-mode luminescence from identical Tb3+ is provided via Gd-sublattice-mediated energy migration and core–shell engineering techniques. By optimizing the structure of a NaGdF4:Yb/Tm@NaGdF4:Ce/Tb nanoarchitecture, both upconversion and downshifting emissions, originating from 5D4 → 7F6,5,4,3 transitions of Tb3+, are achieved through Yb3+ → Tm3+ → [Gd3+]n → Tb3+ and Ce3+ → [Gd3+]n → Tb3+ energy transfer processes, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...