Single-composition white-emitting NaSrBO3:Ce3+,Sm3+,Tb3+ phosphors for NUV light-emitting diodes†
Abstract
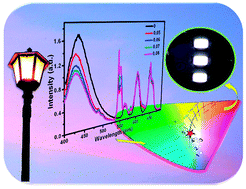
Single-composition (or single-phase) phosphors have been proposed as a new strategy to overcome the concerns of emission reabsorption and different degradation rates of the three primary phosphors for light-emitting diode (LED) applications. A series of Ce3+, Sm3+ and Tb3+ co-doped NaSrBO3 phosphors were synthesized via a high temperature solid-state reaction. Upon near ultraviolet (NUV) excitation, tunable emission from violet to white in the visible region was realized in NaSrBO3:Ce3+,Sm3+,Tb3+ phosphors by controlling the dopant concentrations. Particularly, highly efficient white-light emission with a quantum yield as high as 48.2% was achieved. The energy transfer mechanism between Ce3+ and Sm3+ ions in NaSrBO3 was found to be predominantly of dipole–dipole nature. Moreover, the thermal quenching effect on the photoluminescence of NaSrBO3:Ce3+,Sm3+,Tb3+ was comprehensively surveyed over the range of 300–600 K, showing a good thermal stability for LED applications. By integrating this single-composition white-emitting NaSrBO3:Ce3+,Sm3+,Tb3+ phosphor with a 360 nm NUV chip, we fabricated a high-performance white LED (WLED), which exhibited an excellent color rendering index Ra of 80.1 and a correlated color temperature of 6731 K with CIE coordinates of (0.311, 0.314). These findings demonstrate that the proposed single-composition white-emitting NaSrBO3:Ce3+,Sm3+,Tb3+ phosphors can serve as promising phosphors for NUV-excited WLEDs.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2015 Journal of Materials Chemistry C Hot Papers

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...