A synergistic combination of diatomaceous earth with Au nanoparticles as a periodically ordered, button-like substrate for SERS analysis of the chemical composition of eccrine sweat in latent fingerprints†
Abstract
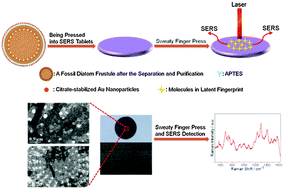
The artistry and the amazingly beautiful hierarchical three-dimensional (3D) patterning of diatoms make them ideal biological scaffolds. Here, fraction-free and ultra-high-purity diatomaceous earth has been successfully prepared by low speed centrifugation in saturated sucrose solution and calcination at 600 °C for 2 h. The prepared citrate-stabilized 18 ± 2.4 and 32 ± 5.4 nm Au nanoparticles were singly, uniformly and densely self-assembled onto amino-functionalized diatomaceous earth templates following their surface morphologies via electrostatic interactions, during which the control experiment and appropriate parameter exploration were performed. The formed 18 ± 2.4 and 32 ± 5.4 nm Au nanoparticle coated diatomaceous earth fine-grained composite materials were pressed into hard, button-like tablets with a fixed diameter of 13 mm and a thickness of 2 mm, and then the two fabricated types of button-like portable tablets were used for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) detection, and their enhancement factors (EFs), SERS reproducibility and long-term stability were testified using rhodamine 6G (R6G) as the probe molecule. The button-like portable tablet composed of diatomaceous earth-templated 32 ± 5.4 nm Au nanoparticle arrays had a higher EF and was successfully applied to SERS analysis of the trace chemical composition of eccrine sweat in latent fingerprints. It may reveal the medical condition of an individual by analyzing the obtained SERS spectra, suggesting that the SERS-based methodology, due to its high sensitivity, has a potentially wide range of applications in fields that need trace detection, such as medical diagnostics and forensic investigations. Moreover, the button-like, 3D periodically ordered tablet as a portable SERS substrate composed of a synergistic combination of diatomaceous earth with Au nanoparticles in this work is robust, easy to carry around, and applicable to on-site SERS detection.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...