Preparation of 4-dicyanomethylene-2,6-distyryl-4H-pyran derivatives, their functional polystyrenes and study of their different aggregation induced emission behaviors†
Abstract
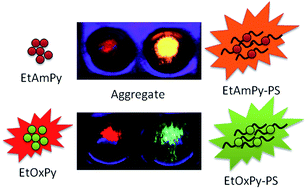
Aggregated or solid state red fluorescent materials with efficient light emission are rare but have wide applications in optoelectronic and biological fields. Herein, two pyran derivatives, EtAmPy and EtOxPy with different charge transfers (CT), were designed as initiators and introduced to polystyrene chains via atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP). The emission of EtAmPy was quenched both in highly polar solvents and in an aggregated state because of its strong CT and intermolecular interactions, respectively. After EtAmPy was introduced to normal polystyrene chains, the obtained functional PS emitted strong red light with a quantum yield of 37% in an aggregated state. Differently from EtAmPy, EtOxPy, possessing a weak CT and not being sensitive to the change of microenvironment, was AIE-active and displayed a large red shift in emission spectra in an aggregated state. Meanwhile, the functional PS initiated by EtOxPy showed obviously blue-shifted emission, compared to its initiator, in an aggregated state by reducing their intermolecular interactions. EtAmPy-functionalized polystyrene showed a successful application in cell imaging. Therefore, using the CT effect in molecular design and polymerization is beneficial to obtaining new red emission probes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...