Electrical and optical properties of 4-N,N-dimethylamino-4′-N′-methyl-stilbazolium tosylate (DAST) modified by carbon nanotubes†
Abstract
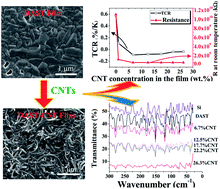
4-N,N-Dimethylamino-4′-N′-methyl-stilbazolium tosylate (DAST) is an important nonlinear optical and terahertz sensitive material, but its poor conductivity and extreme process for crystal growth limit practical applications. To tackle these problems, we designed and prepared novel binary composite films that are composed of two-dimensional DAST and one-dimensional carbon nanotubes (CNTs). Our preparation method is simple, reproducible, and compatible with the existing device fabrication technology. The chemical structures and physical properties of the as-prepared thin films were systematically investigated. Results indicate that the electrical conductivity and optical response in a broad region from visible light to terahertz are significantly enhanced after addition of CNTs to DAST. However, either too small or too large CNT loading in the composite will lead to degradation of the properties. In contrast, the composite film with a medium CNT content of 6.7 wt% exhibits optimal comprehensive properties that are favorable for detector applications. This work discloses valuable results about the novel DAST-based films, their chemical structures, electrical and optical properties, synergistic effects of DAST and CNTs, and a simple preparation method, all of which will be helpful for better understanding of the DAST and seeking new optoelectronic sensitive materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...