Towards microstructured optical fibre sensors: surface analysis of silanised lead silicate glass†
Abstract
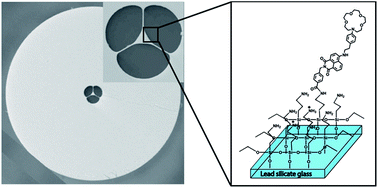
While protocols to surface functionalise silica glass platforms are well-established, the surface coating of other glass types has received limited attention. Here we fully characterise the surface attachment of a fluoroionophore on extruded lead silicate glass slides and demonstrate these slides as a model for investigating the surface chemistry in a microstructured optical fibre (MOF). This model system allows the utilization of multiple, complementary surface-sensitive techniques that cannot be used within the internal surface of the fibre structure. By characterising the fluoroionophore attachment, we observe that the fluorescence intensity from fluorescence imaging, the atomic nitrogen percentage measured by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), the carbonyl bond component (287.5 eV) in the XPS high resolution carbon spectrum, and Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of the time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) data can be used to provide relative quantification of the concentration of an attached fluoroionophore. We also show the first use of ToF-SIMS imaging and depth profiling of the Pb content within a glass substrate to provide information on the coverage provided by the coating and the relative thickness of an organic coating. Combined together, these techniques provide a comprehensive picture of the coated glass surface that facilitates fibre sensor development.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...