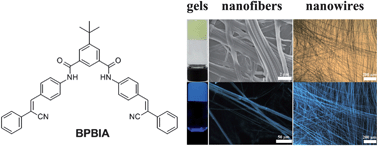
A V-shaped cyanostilbene amide derivative (BPBIA) containing tert-butyl groups has been designed and synthesized. It was employed as building blocks to fabricate one-dimensional (1D) organic nano- or microstructures. BPBIA shows excellent self-assembling properties. First, it can readily self-assemble into gels with nanofiber structures in several kinds of organic solvents through the cooperative effect of intermolecular hydrogen bonding, π–π stacking and cyano interactions. Second, size controllable well-defined 1D nanowires with lengths up to several millimeters also have been fabricated based on the slow evaporation approach. More importantly, the individually dispersed nanowires with uniform morphology are independent of substrates and solvents. Compared with the solution, both the generated nanofibrous gels and the nanowires exhibited significantly enhanced emission, showing typical aggregation-induced emission (AIE) behavior. The single-crystal X-ray analysis provided a reasonable explanation for the formation of 1D nano- or microstructures. Thus, the molecule could provide ways for the easy fabrication of highly emissive nano- and microstructures for use in organic optoelectronics.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...