Biodegradable methacrylated casein for cardiac tissue engineering applications
Abstract
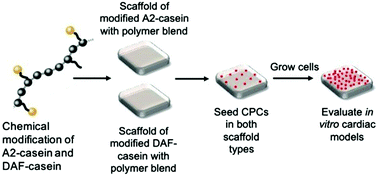
Casein is a naturally derived amino group (–NH2) rich protein, that enables surface functionalization leading to hydrophilicity, which in turn facilitates better cell adhesion. Casein obtained from either commercial β-casein rich skim milk (A2 milk) or dissolved air flotation (DAF) technology was tested for its potential for tissue engineering applications in a comparative study. A novel biodegradable biomaterial was synthesized from casein by chemically modifying with methacrylic anhydride (MA) and combined with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) blend. The resulting methacrylated casein (CasMA) with the two polymers was processed into porous scaffolds with low and high MA concentrations to demonstrate CasMA's ease of modification and reproducibility. Fourier Transform Infrared Microscopy (FTIR) and Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR) revealed the presence of all the components and the successful modification of casein. The rheological and morphological analysis presented viscous behaviour and columnar hollow tube-like microstructures in agreement with the biomaterials’ swelling and biodegradation behaviour. The live/dead in vitro assay showed high cell viability that agreed with the cell proliferation (MTT) assay in vitro, which indicated increased proliferation upon casein modification at appropriate biomaterial concentrations and volumes. This study not only showed a possible mechanism of casein methacrylation but also presented the potential use of waste materials like DAF-casein as a value-added product for tissue engineering applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry B HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...