Efficient enzyme-activated therapy based on the different locations of protein and prodrug in nanoMOFs†
Abstract
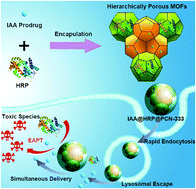
Enzyme-activated prodrug therapy (EAPT) is an effective cancer treatment strategy able to transport non-toxic prodrugs and subsequently convert them into drugs at specific times and locations. However, due to the limitation of easy biodegradability and the membrane-impermeable characteristic of exogenous enzymes, there is a need to exploit suitable carriers for the effective protection and simultaneous delivery of activating enzymes into cancer cells. Herein, hierarchically porous MOFs were employed for the loading of enzyme and prodrug in a single nanocarrier thanks to their different cavity sizes. The simple loading process allows entrapping of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and a monocarboxyl-containing indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) prodrug with high loading capacities in different spaces, which keeps the catalytic activity of the enzyme perfectly intact and avoids the premature activation of the prodrug. The encapsulated HRP and IAA exhibit sustained and synchronized release behaviors. Compared to the native HRP enzyme, the current MOF nanocarriers not only facilitate enzyme delivery into cellular lysosomes and subsequent endosomal escape, but also effectively release enzyme and prodrug in the intracellular environment within 48 h. Eventually, HRP and IAA loaded MOF nanocarriers cause significant cell death with a low IC50 of 4.2 mg L−1, while the IAA prodrug alone is non-toxic even at high concentrations. Thus, hierarchically porous MOFs might offer a promising platform for EAPT with a highly consistent spatiotemporal distribution of enzymes and prodrugs in target tissues.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...