Self-defending additively manufactured bone implants bearing silver and copper nanoparticles
Abstract
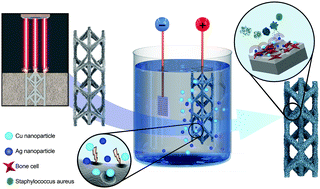
Effective preventive measures against implant-associated infection (IAI) are desperately needed. Therefore, the development of self-defending implants with intrinsic antibacterial properties has gained significant momentum. Biomaterials biofunctionalized with silver (Ag) have resulted in effective antibacterial biomaterials, yet regularly induce cytotoxicity. In this study, the use of both Ag and copper (Cu) nanoparticles (NPs) on TiO2 surfaces was investigated to generate antibacterial and osteoconductive biomaterials. Hence, additively manufactured Ti–6Al–4V volume-porous implants were biofunctionalized with plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) through the incorporation of varying ratios of Ag and/or Cu NPs in the TiO2 layer covering the implant surface. For all experimental groups, the surface morphology, chemical composition, ion release profile, generation of reactive ion species, antibacterial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in vitro and ex vivo, as well as the response of pre-osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells in metabolic activity and differentiation assays were determined. PEO biofunctionalization resulted in rough and highly porous surfaces that released Ag and Cu ions for 28 days and generated hydroxyl as well as methyl radicals. A strong synergistic bactericidal behavior between Ag and Cu ions was detected, which allowed to decrease the concentration of Ag ions by 10-fold, while maintaining the same level of antibacterial activity. Antibacterial agar diffusion and quantitative assays indicated strong antibacterial activity in vitro for the implants containing Ag and Ag/Cu, while no antibacterial activity was observed for implants bearing only Cu NPs. Moreover, the biofunctionalized implants with ratios of up to 75% Ag and 25% Cu NP totally eradicated all bacteria in an ex vivo model using murine femora. Meanwhile, the biofunctionalized implants did not show any signs of cytotoxicity, while implants bearing only Cu NPs improved the metabolic activity after 7 and 11 days. The biomaterials developed here, therefore, exploit the synergistic behavior of Ag and Cu to simultaneously offer strong antibacterial behavior while fully mitigating the cytotoxicity of Ag against mammalian cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...