Intelligent antibacterial surface based on ionic liquid molecular brushes for bacterial killing and release†
Abstract
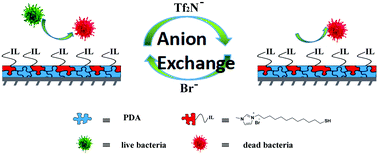
The prevention of bacteria-induced infections has been increasing in importance in both clinical surgery and biomedical engineering. Although great attention has been paid to designing intelligent antibacterial surfaces, the fabrication processes are still not facile and universal enough, and the antibacterial efficiencies of these surfaces are also not ideal. Herein, ionic liquid (IL) molecules of 3-(12-mercaptododecyl)-1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium bromide (IL(Br)) were synthesized with the minimum inhibitory concentrations as low as 4 and 8 μg mL−1 against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Escherichia coli (E. coli), respectively. By simply immersing a polymeric substrate into the IL(Br) solution, an antibacterial surface with high killing efficiency of 99% against S. aureus (94% against E. coli) was achieved via a mussel-inspired approach. Subsequently, 97% S. aureus and 95% E. coli on the substrate could be released by simple ion-exchange of Br− with (CF3SO2)2N− due to the ion sensitivity of the IL molecular brushes. Thus, the proposed facile strategy towards a superior efficiency surface could be potentially used in intelligent antibacterial fields.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...