Glucose oxidase and polydopamine functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles: combination of the photothermal effect and reactive oxygen species generation for dual-modality selective cancer therapy†
Abstract
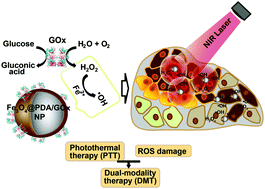
Cancer cells possess some inherent characteristics, such as glucose-dependence and intolerance to heat and exogenous reactive oxygen species (ROS). In this study, a strategy has been developed to target these vulnerable weaknesses of cancer cells using glucose oxidase (GOx) and polydopamine (PDA) functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4@PDA/GOx NPs). PDA is first deposited on the surfaces of iron oxide NPs through self-polymerization, and then GOx is covalently linked with PDA upon mixing the enzyme and Fe3O4@PDA under alkaline conditions. In this system, the PDA layer along with iron oxide NPs serves as a photothermal transfer material converting near infrared (NIR) radiation into heat. The covalently linked GOx can competitively consume glucose and spontaneously generate ROS H2O2 that can be further converted by the iron oxide NPs into more toxic ˙OH, inducing apoptosis of cancer cells. The selective toxicity of Fe3O4@PDA/GOx NPs on cancer cells is demonstrated both in vitro and in vivo. In particular, a single injection rather than multiple doses results in significant suppression of tumors, and does not induce apparent histological lesions in the 4T1 tumor-bearing Balb/c mice. The versatility of the functionalization strategy reported in this study will contribute to developing efficient therapies for selective cancer treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...