Subcellular co-delivery of two different site-oriented payloads based on multistage targeted polymeric nanoparticles for enhanced cancer therapy†
Abstract
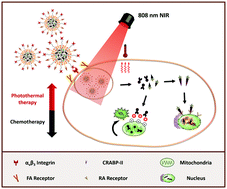
The co-delivery of two or more anti-tumor agents using nanocarriers has shown great promise in cancer therapy, but more work is needed to selectively target drugs to specific subcellular organelles. To this end, our research has reported on “smart” polymeric nanoparticles that can encapsulate two different site-oriented pro-drug molecules, allowing them to reach their targeted subcellular organelles based on NIR-mediated controlled release, allowing for targeted modifications in the nucleus or the mitochondria. Specially, an all-trans retinoic acid (RA) conjugated cisplatin derivative (RA–Pt) can be delivered with high affinity to the nucleus of target cells, facilitating the binding of cisplatin to double-stranded DNA. Similarly, a synthesized derivative generated by conjugation of triphenylphosphine (TPP) and celastrol (TPP–Cet) may facilitate mitochondrial targeted drug delivery in tumor cells, inducing ROS accumulation and thereby leading to apoptosis. Relative to nanoparticles loaded with a single therapeutic agent, dual antitumor agent-loaded nanocarriers showed promising synergy, exhibiting significant tumor inhibition in vivo (81.5%), and less systemic toxicity than the free therapeutic agents alone or the drug-loaded nanoparticles without targeted ligands. These results indicated that site-oriented payloads can effectively enhance antitumor therapeutic efficiency and these studies offer a novel “multistage targeted-delivery” strategy in synergistic therapy for cancer treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...