Pyrrolopyrrole aza boron dipyrromethene based two-photon fluorescent probes for subcellular imaging†
Abstract
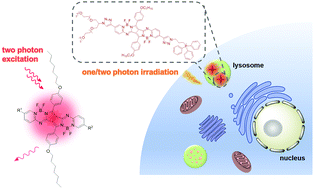
A series of pyrrolopyrrole aza boron dipyrromethene derivatives have been designed and synthesised as two-photon fluorescent probes. The bisalkynyl analogues, having a donor–π–donor quadrupolar skeleton, show a red-shifted Q band at ca. 700 nm in toluene and a two-photon absorption (TPA) cross-section up to 2349 GM at 1040 nm. To enable these dyes to be used for subcellular imaging, a branched oligoethylene glycol unit has been introduced to enhance their hydrophilicity and biocompatibility, and a potential organelle-selective group, namely triphenylphosphonium or morpholine moiety has also been added with a view to targeting the mitochondria or lysosomes respectively. The resulting conjugates are essentially non-aggregated in deionised water, exhibiting an intense Q band at 668 nm and a TPA cross-section up to 384 GM at 1040 nm. These spectral features have been analysed using density functional theory calculations, which suggest that the TPA is mainly due to the S0 → S2 transition. In the subcellular imaging study, it has been found that the triphenylphosphonium-containing derivative can localise in the lysosomes of HeLa human cervical carcinoma cells, which may be a result of its positive charge and the negative log P value (−2.46, P = partition coefficient), while the morpholine-substituted analogue does not exhibit preferential subcellular localisation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...