Facile synthesis of near-infrared emitting dBSA-templated Cu nanoclusters for sensitive detection of heparin†
Abstract
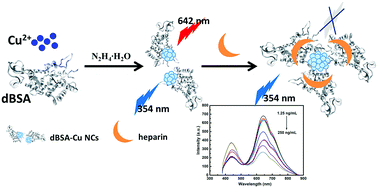
Heparin is the most widely studied glycosaminoglycan. It plays an important role in regulating several normal physiological and pathological processes, including inhibition of thrombocytopenia, lipid regulation, metabolism and electrostatic attraction with various proteins. Hence, it is crucial to develop selective and sensitive assays for monitoring heparin levels in biological systems. In the present study, we designed a facile synthesis method to prepare near-infrared emitting denatured bovine serum albumin-templated copper nanoclusters (dBSA-Cu NCs) for the trace detection of heparin. In aqueous solution, the bovine serum albumin (BSA) was denatured by heating at a temperature of 70 °C to prepare dBSA, which was employed as the template for fabricating the dBSA-Cu NCs. Then, Cu2+ ions were directly reduced to dBSA-Cu NCs by hydrazine hydrate at room temperature. The synthetic process was very simple to control due to the lack of any complicated procedure, such as heating or adjusting pH. In addition, the fluorescence intensity of dBSA-Cu NCs at 642 nm was quenched by heparin samples. Hence, the dBSA-Cu NCs can be used as a probe for the trace detection of heparin with a very low limit of detection (LOD) of 0.26 ng mL−1 in a linear range from 1.25 ng mL−1 to 250 ng mL−1. Furthermore, the as-developed dBSA-Cu NCs were also successfully applied to determine heparin in human plasma samples with quantitative spike recoveries from 95% to 104%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...