Real-time noninvasive monitoring of cell mortality using a two-photon emissive probe based on quaternary ammonium†
Abstract
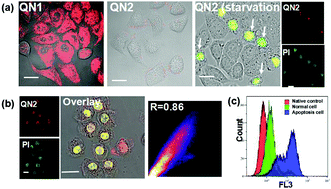
We report that a dicyanyl derivative QN2 containing quaternary ammonium was capable of identifying apoptotic cells by targeting nucleic acid (DNA and RNA) and we were able to observe nuclear ultra-details using a stimulated emission depletion (STED) nanoscopy technique. QN2 could evaluate the anti-cancer drug pesticide effect by monitoring in real-time without interfering with normal cell proliferation. These results suggest the high potential for using QN2 in practice for monitoring apoptosis to evaluate tumor therapy effectiveness or for drug development.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...