Antigen detection with thermosensitive hydrophilicity of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-grafted poly(vinyl chloride) fibrous mats
Abstract
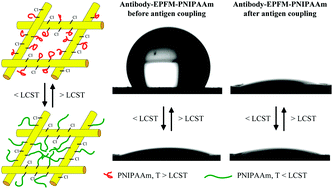
Poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) was electrospun as fibrous mats to treat with NaN3. The secondary chlorines of PVC were modified to generate azido-terminated electrospun PVC fibrous mats (EPFMs). Sequentially, propargyl-terminated poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) was further synthesized and grafted onto the azido-terminated EPFMs via a click reaction resulting in a scale-like structure on the fibers. The static water contact angles (SWCAs) of the grafted EPFMs reached 0 and 140° when the working temperatures were 25 and 45 °C, respectively. In contrast to the grafts on a smooth surface, the change in SWCA from 25 to 45 °C was enhanced significantly. EPFMs with PNIPAAm grafts could immobilize an antibody (antiHA), and they could be used for an immunosorbent assay. After coupling with an antigen (HRP-HA) at 80 ng mL−1 for 8 min, the hydrophobicity of EPFMs with PNIPAAm grafts disappeared completely at 45 °C. In addition, the grafted EPFMs exhibited a much more dark blue color than those without the PNIPAAm grafts. SWCA below 10° at 45 °C could be exploited as an index to determine the limit of detection (LOD) as 80 ng mL−1. The immunosorbent assay of EPFMs with PNIPAAm grafts experimentally exhibited high potential in a simple set-up for biosensing due to the unique sensitivity and selectivity of the grafted EPFMs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...