Graphene oxide as a dual Zn/Mg ion carrier and release platform: enhanced osteogenic activity and antibacterial properties
Abstract
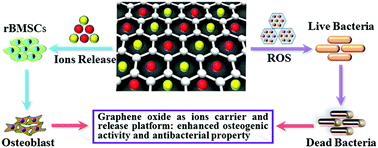
Implant failure of titanium and its alloys still occurs due to insufficient osseointegration and implant associated infections. Therefore, titanium implants with enhanced osseointegration and antibacterial activities are desirable. To achieve this goal, graphene oxide (GO) as a dual zinc/magnesium (Zn/Mg) ion carrier and release platform was constructed on the titanium surface by cathode electrophoresis deposition. Rat bone mesenchymal stem cells were used to investigate the osteogenic activity. Gram-negative E. coli was utilized to assess the antibacterial activities. Results show that GO co-doped with Mg and Zn ions with a sustained and slow release exhibited the best osteogenic activity among all the samples by stimulating the expressions of osteogenesis related genes containing alkaline phosphatase (ALP), type I collagen (Col-I), osteocalcin (OCN), and osteopontin (OPN), and by promoting the alkaline phosphatase activity and extracellular matrix mineralization. The existence of GO endowed titanium with superior antibacterial activities against Gram-negative E. coli. Due to the synergistic effects of GO, Mg and Zn ions, a titanium surface with enhanced osseointegration and antibacterial activities was achieved.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...