Engineering a protein-based nanoplatform as an antibacterial agent for light activated dual-modal photothermal and photodynamic therapy of infection in both the NIR I and II windows†
Abstract
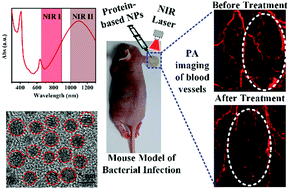
The rapid rise of drug- and multi-drug resistant pathogenic bacteria constitutes an increasing risk to global public health. Thus, it is essential to develop new agents and/or strategies to overcome the antibiotic resistance crisis. Herein, ultra-small protein-based nanoparticles (NPs) with absorption covering both the near-infrared (NIR) I and II windows were constructed as novel antibacterial agents, which introduced a killing strategy utilizing the synergistic photothermal and photodynamic effects. The agent engineered by the conjugation of Ce6 molecules to ultra-small hydrophilic protein-modified copper sulfide NPs can transfer light energy into thermal energy for photothermal therapy and produce reactive oxygen species for photodynamic therapy. Under the irradiation of both NIR I and II lasers, the agent demonstrated a potent bacteria killing activity on both Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus) and Gram-negative (Escherichia coli) in vitro bacteria with high efficacy and safety. Furthermore, the as-prepared NPs also displayed an efficient in vivo bactericidal activity in a mouse model as monitored by measuring the photoacoustic signals of the blood vessels around the infection site. Consequently, leveraging the synergistic photothermal and photodynamic effects, the as-designed ultra-small NIR NPs may eliminate the emergence of drug resistance due to the mechanical destruction of the bacteria cell, thus representing a promising approach to control the antibiotic resistance crisis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...