Bismuth ferrite-based photoactive materials for the photoelectrochemical detection of disease biomarkers coupled with multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles
Abstract
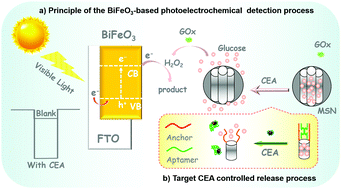
This work designs a new photoelectrochemical (PEC) sensing system for the detection of carcinoembryonic antigens (CEAs) using bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3) nanostructures as photoactive materials, accompanied by the target-controlled release of glucose from multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) for signal amplification. Glucose molecules were gated in the pores via the hybridization of a CEA aptamer with anchor DNA (aDNA, modified on the mesoporous silica nanoparticles). Upon the addition of the target CEA, the analyte competitively reacted with the aptamer to open the gate, thus resulting in the release of glucose molecules from the MSNs. Based on the oxidization of glucose in the presence of glucose oxidase, the as-generated enzymatic product (H2O2) served as an electron acceptor to enhance the photocurrent generated by the BiFeO3 nanostructures under visible light irradiation. In this way, an in situ amplified photocurrent could be achieved in that the low-concentration target CEA could cause the release of numerous glucose molecules. Experimental results suggested that the photocurrent obtained from the BiFeO3-based photoactive materials increased with increasing CEA concentration and showed a good linear dependence on the logarithm of the CEA level from 5.0 pg mL−1 to 50 ng mL−1 under optimal conditions. Additionally, the BiFeO3-based PEC sensing platform also showed good stability and favorable selectivity, and satisfactory accuracy for CEA detection in human serum specimens in comparison with a reference CEA ELISA kit. The good analytical performance of the BiFeO3-based PEC sensing method makes it a promising tool for the efficient, low-cost and convenient detection of CEAs in disease diagnosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...