Complex shape deformations of homogeneous poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/graphene oxide hydrogels programmed by local NIR irradiation†
Abstract
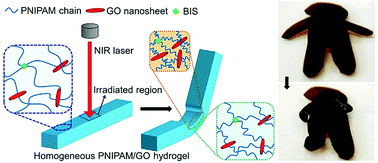
Stimuli-responsive hydrogels, with programmable shape deformations upon external stimuli, have promising applications in diverse fields. Complex shape deformation through precise remote control of the direction, position and degree of deformation is critical for practical applications. Herein, we describe a novel and facile method that enables remote and instant programming of the deformation direction, position and degree of homogeneous poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/graphene oxide (PNIPAM/GO) nanocomposite hydrogels through local near infrared (NIR) laser irradiation. Under NIR irradiation, GO nanosheets absorb NIR light, which transforms into heat and induces the phase transition of PNIPAM. Due to the slow heat transfer of the hydrogels, the irradiated part of the PNIPAM/GO hydrogels shrinks more than the un-irradiated part, leading to the folding or bending of the gels toward the irradiated part. The deformation degree of the hydrogels can be adjusted by changing the composition (e.g., GO concentration) or the thickness of the hydrogels and the irradiation parameters, including power density of NIR laser and irradiation time. Impressively, by simply programming the local irradiation on different parts of hydrogel strips, sheets and gel samples with other shapes, the hydrogel samples can undergo complex shape deformations from 1D to 2D and 2D to 3D, and imitate the postures of a human and the closing of the leaves of mimosa.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...