Surface modification strategies for combating catheter-related complications: recent advances and challenges
Abstract
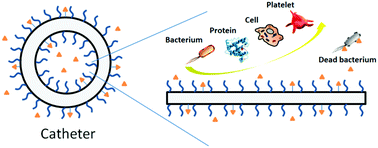
Indwelling medical devices such as catheters are a ubiquitous and indispensable component in modern medical practice for improving therapeutic outcomes for patients. Yet at the same time, they can be a cause of healthcare-associated infections contributing to patient morbidity and mortality, and healthcare costs. Other surface-related complications can also arise from interactions of the catheter with biological components in the in vivo environment. This review summarizes the progress made in the development of antimicrobial surfaces, and the application of surface modification strategies to three important classes of catheters: urinary catheters, intravascular catheters and peritoneal dialysis catheters. The review also provides a perspective on the challenges in translating favorable developments from in vitro studies into similar clinical outcomes.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...