An emerging dual collaborative strategy for high-performance tumor therapy with mesoporous silica nanotubes loaded with Mn3O4†
Abstract
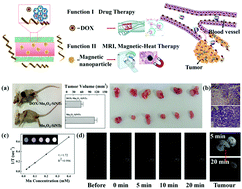
A highly integrated nanocomposite is constructed based on mesoporous silica nanotubes (SiNTs)-loaded with Mn3O4 nanoparticles for cervical cancer therapy via T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and doxorubicin-based chemotherapy. Mn3O4 magnetic nanoparticles uniformly distributed within SiNTs can effectively detect the tumor microenvironment, as revealed by clinical T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. The SiNTs possessed a high loading rate for doxorubicin (DOX) and a simultaneous pH-dependent response release, mainly due to the electrostatic interaction between DOX molecules and the mesoporous silica surface. According to MTT assay, confocal laser scanning microscopy and bio-TEM observations, the cellular uptake of the as-prepared DOX–Mn3O4–SiNTs was both dose- and time-dependent, and the SiNTs were accumulated mostly in lysosomes. Further pathological examinations revealed that the DOX–Mn3O4–SiNTs multifunctional drug delivery system led to remarkably destructed cells, large vacuoles, and irregular widening of tumor tissues. This collaborative strategy could pave the way towards high-performance nanotherapeutics with superior antitumor efficacy and reduced side effects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...