A synthetic bridging patch of modified co-electrospun dual nano-scaffolds for massive rotator cuff tear
Abstract
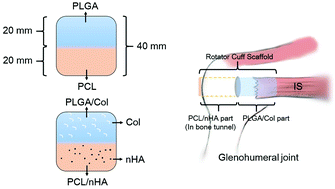
Massive rotator cuff tears (MRCTs) are difficult to repair because of the retraction and poor mobility of torn tendons. In the current study, co-electrospun dual nano-scaffolds of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/collagen I-polycaprolactone/nanohydroxyapatite (PLGA/Col-PCL/nHA) were fabricated and used to bridge MRCTs of infraspinatus tendons in a rabbit model. PLGA–PCL served as a control. The PLGA or the PLGA/Col sides of the dual scaffolds connected the tendon stumps. The PCL or PCL/nHA side was inserted into the bone tunnel at the insertion of the infraspinatus tendon. Fibroblasts showed higher viability and collagen secretion when seeded on a PLGA/Col scaffold compared to a PLGA scaffold. Osteoblasts seeded on a PCL/nHA scaffold grew better with higher mineralization than on a PCL scaffold. Histologically, collagen regenerated along PLGA scaffolds, but showed poor ingrowth to scaffolds compared with the PLGA/Col group. Newly formed bone was observed on the PCL scaffold, but was less than that on the PCL/nHA scaffold. At 6 weeks post repair, the regenerated tendon in both groups had similar maximum load to failure and ultimate stress but significantly lower stiffness in the PLGA–PCL group and a higher cross-sectional area in the PLGA/Col-PCL/nHA group compared with normal values. At 12 weeks, the maximum failure load, ultimate stress and cross-sectional areas of the regenerated tendon in the PLGA/Col-PCL/nHA group were significantly higher than in the PLGA–PCL and normal groups. The biomechanical properties of the PLGA–PCL group were similar to normal except for a larger cross-sectional area. Our data showed that the co-electrospun dual nano-scaffolds are promising in bridging MRCTs. Doping with Col and nHA further strengthens tissue regeneration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...